
Scientific Preprint (Under Review)
We share an open-access preprint that reviews Procyanidin C1 as a dual-mode senotherapeutic candidate. The paper is currently under peer review and reflects early scientific analysis. Readers are welcome to download the document, recognizing that findings are preliminary and require further validation before drawing conclusions.
Dual-phase activity in preclinical studies
Mechanistic Synopsis of PCC1
PCC1 demonstrates a dual mechanism: senomorphic effects at lower concentrations and selective clearance at higher levels. Research in preclinical models highlights pathways such as BCL-2 regulation, ROS thresholds, and SASP suppression. These findings suggest PCC1 may influence multiple organs and systems. Evidence remains limited to laboratory and animal studies, requiring further validation before clinical translation.
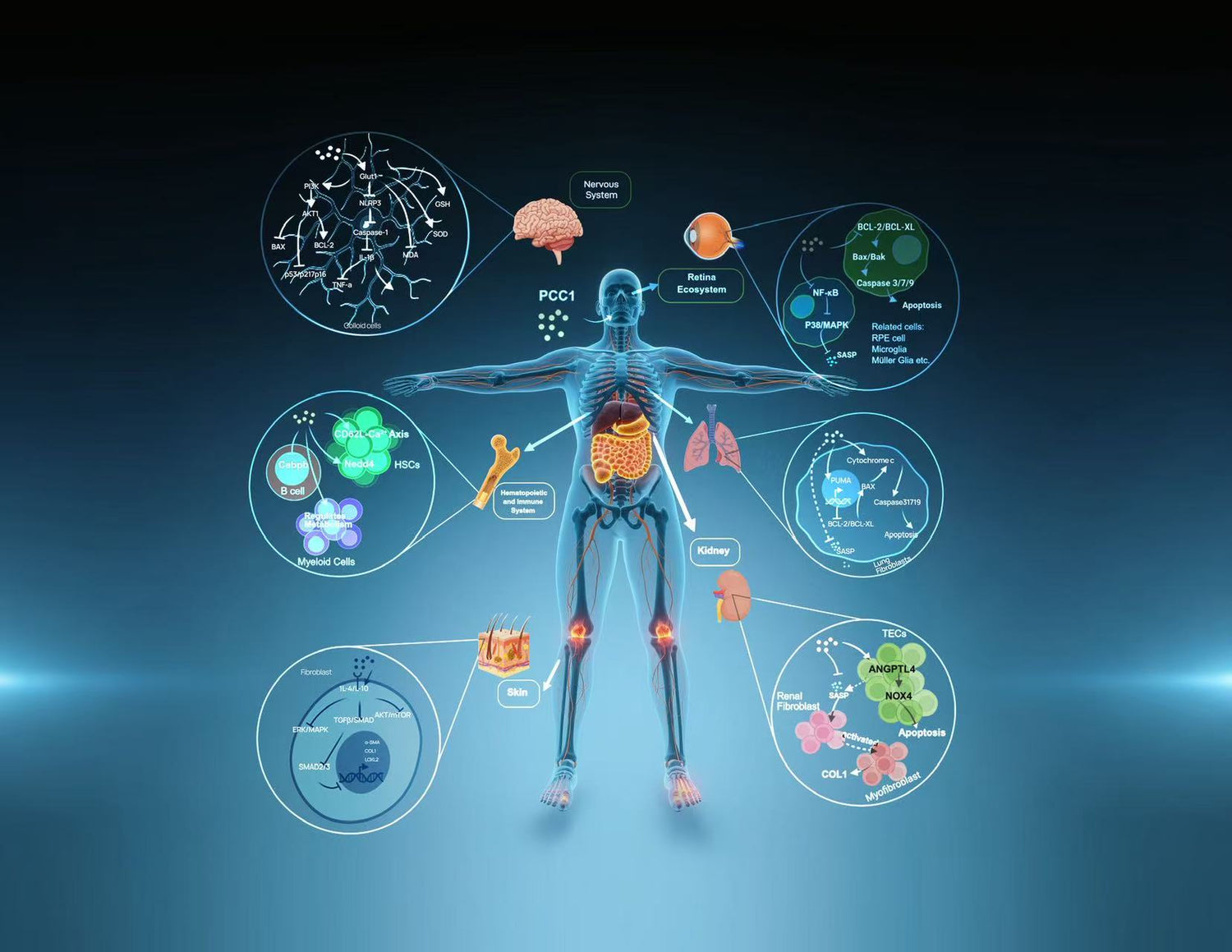
Observations in aging models
Biomarker Research on PCC1
Preclinical research on PCC1 has examined its influence in multiple animal and cellular models. Findings suggest changes in markers such as SA-β-Gal, p16/p21, IL-6, and TNF-α, as well as improvements in oxidative balance and apoptosis-related proteins. These results highlight PCC1’s broad experimental profile. However, evidence is limited to controlled laboratory contexts, and translation to human outcomes requires further investigation.

PCC1 among key candidates
Senolytic Research Overview
This comparative overview examines PCC1 in relation to other senolytic candidates including Dasatinib + Quercetin, Fisetin, Navitoclax, and Piperlongumine. The analysis covers mechanisms of action, dosing concepts, and safety considerations observed in preclinical research. PCC1 is characterized by dual-phase modulation and a favorable safety window, positioning it as a distinct candidate. The evidence remains exploratory and is derived from animal and cellular studies.

Tolerability across agents
Safety Profile of PCC1
Safety analysis indicates PCC1 may have a broader margin of tolerability compared to other senolytics. Studies suggest limited hematologic burden, minimal cardiovascular or gastrointestinal stress, and no strong organ toxicity signals in experimental models. Unlike compounds such as Navitoclax or Dasatinib, PCC1 shows fewer acute risks in reported preclinical observations. These findings are early-stage and should be viewed as exploratory, not conclusive evidence for human use.

Phytosomal formulations
PCC1 Delivery Advances
A key challenge for PCC1 is limited bioavailability. Research into innovative delivery systems, such as phytosomal lecithin formulations, has shown improved stability, digestive retention, and absorption in experimental models. Results include higher blood concentration peaks and longer active intervals compared to unformulated PCC1. These technological advances highlight strategies to enhance effectiveness in laboratory settings, though human efficacy remains to be demonstrated.
